✈️ Crosswind Calculator
Calculate crosswind and headwind/tailwind components for safe aviation decisions.
Crosswind
Headwind / Tailwind
Gust Crosswind
Recommendation
Wind vs Runway
Crosswind in aviation refers to wind blowing perpendicular to the runway direction, creating challenges particularly during takeoff and landing. Understanding and managing crosswind is crucial for flight safety and effective flight planning.
- Crosswind affects an aircraft’s ability to maintain alignment with the runway, requiring pilots to apply specialized techniques to control drift and ensure safe landings.
- Proper assessment of wind components can prevent accidents and runway excursions, safeguarding both aircraft and passengers.
Our crosswind calculation tool helps pilots quickly and accurately determine the crosswind, headwind, and tailwind components for any runway and wind conditions. This headwind and tailwind calculator is an essential part of aviation wind calculator online tools that enhance situational awareness and safety.
By using this tool, pilots and aviation students can optimize their flight plans, confidently manage wind effects, and improve overall operational safety. If you’re also looking for quick online calculators outside aviation, check out our Blooket Calculator for instant results.
What is a Crosswind?
A crosswind in aviation is simply wind blowing at an angle that’s not aligned with the runway—typically perpendicular to it. This means instead of coming straight down or up the runway, the wind hits the aircraft from the side, influencing its direction during takeoff and landing.
Headwind vs Tailwind vs Crosswind
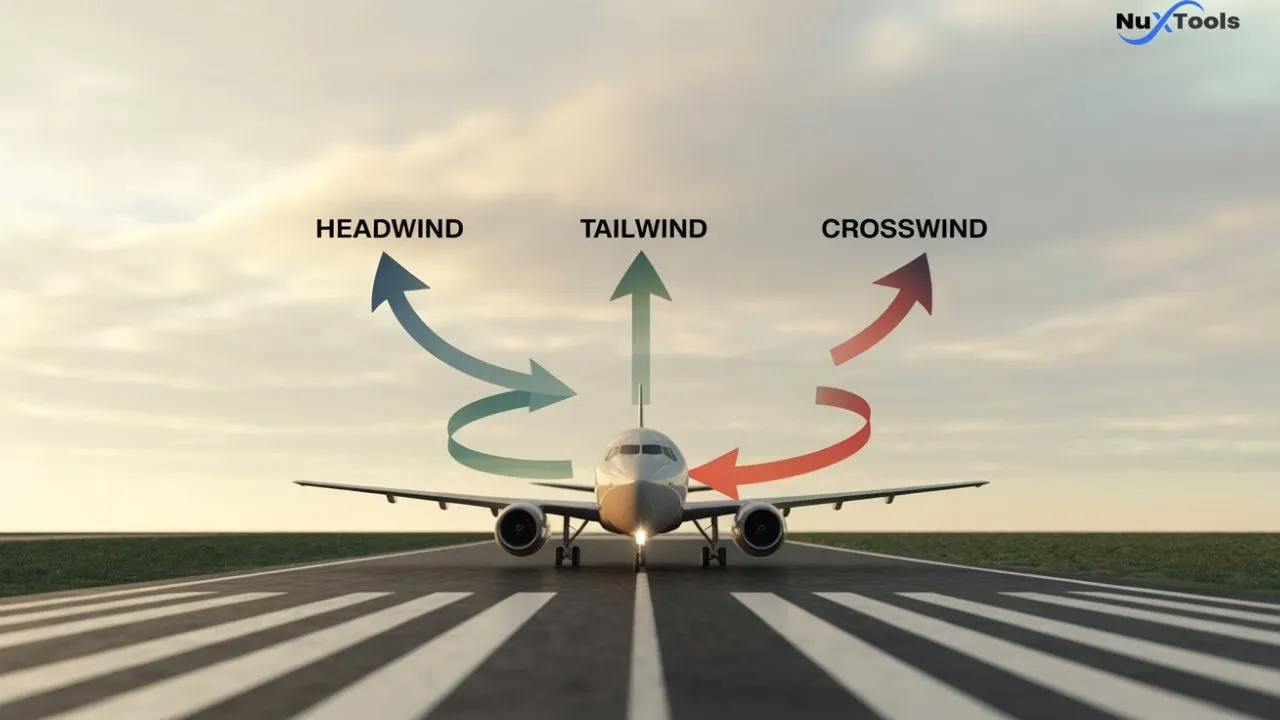
Understanding the difference between headwind, tailwind, and crosswind is essential for safe flight operations:
- Headwind: Wind blowing directly against the aircraft’s forward motion along the runway. It generally helps by reducing takeoff and landing distances.
- Tailwind: Wind blowing in the same direction as the aircraft’s travel—this can increase required runway length and affect safety margins.
- Crosswind: Wind blowing sideways across the runway, requiring pilots to correct the aircraft’s course to maintain runway alignment.
Why Knowing Crosswind Matters
- Crosswinds require pilots to perform special landing techniques and corrections to avoid drifting off the runway crosswind landing tips from AOPA.
- Failure to manage crosswinds properly can lead to dangerously uneven landings or runway excursions.
- Using a crosswind calculation tool helps pilots quantify the crosswind component, aiding crucial decisions during flight planning and real-time operations.
- Tools like the headwind and tailwind calculator and aviation wind calculator online provide quick, reliable data that improves safety and confidence in varying wind conditions.
Why Pilots Need a Crosswind Calculator

Flying safely in windy conditions requires pilots to understand their aircraft’s limits and precisely measure wind components. Different aircraft types—like light general aviation (GA) planes and larger airline jets—have varying safe crosswind limits FAA Guide for aircraft that pilots must respect to ensure smooth takeoffs and landings.
- Light GA aircraft often have lower crosswind tolerance, meaning pilots need to be extra cautious when wind components approach these limits.
- Airline pilots work with larger jets that typically handle stronger crosswinds but still must observe maximum demonstrated crosswind guidelines for safety.
- Manually using crosswind component chart alternatives like printed charts or mental math takes time and can introduce errors during critical flight phases.
A modern pilot wind calculation tool streamlines this process by instantly computing the exact crosswind and headwind/tailwind components based on wind speed, direction, and runway heading. This saves valuable time, reduces mental load, and provides clear safety status—whether the wind conditions are:
OK
CAUTION
EXCEED
By using a reliable crosswind calculator, pilots can quickly assess whether conditions fall within safe operational limits, enabling informed decisions that prioritize safety and flight efficiency.
How the Crosswind Calculator Works (Behind the Tool)
Understanding how the crosswind calculator works helps pilots and students appreciate the accuracy and speed it delivers compared to manual methods.
- Angle Normalization: The tool first calculates the angle difference between the wind direction and the runway heading. This angle is normalized to ensure it stays within 0 to 360 degrees for accurate calculations. This process is why it’s sometimes called a wind direction and runway heading calculator.
- Trigonometric Calculations: Using trigonometry, the crosswind component is found by multiplying the wind speed by the sine of the angle difference:
Crosswind=Wind Speed×sin(θ)Crosswind=Wind Speed×sin(θ)
Similarly, the headwind or tailwind component is calculated using the cosine of the angle:
Headwind/Tailwind=Wind Speed×cos(θ)Headwind/Tailwind=Wind Speed×cos(θ)
This ensures precise separation of wind effects relative to the runway.
- Gust Factor Calculation: If a gust speed is provided, the calculator applies the same trigonometric principles to estimate the gust crosswind component, giving pilots a more comprehensive wind profile.
- Accuracy vs Manual Charts: Compared to traditional crosswind component chart alternatives, this digital tool reduces human error and speeds up the process. Manual lookup tables and chart estimations rely on assumptions and approximations, while the calculator uses exact angle and speed values for better accuracy.
Inputs You Provide in the Calculator
To accurately calculate the crosswind and headwind or tailwind components, the aviation wind calculator online requires several essential inputs from the user:
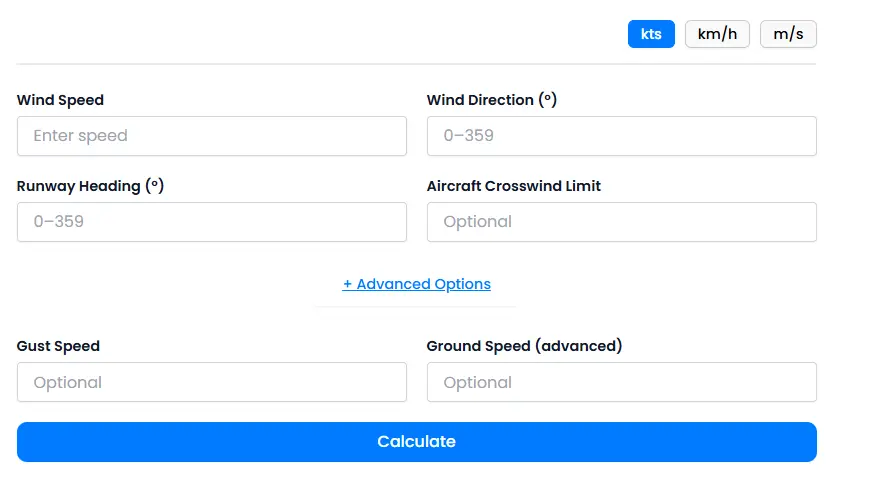
- Wind Speed: The velocity of the wind affecting the runway environment, typically entered in knots, km/h, or m/s.
- Wind Direction (°): The angle from which the wind is blowing, measured in degrees from 0 to 359; critical for determining wind’s impact relative to the runway.
- Runway Heading (°): The orientation of the runway, also measured in degrees, to compare against wind direction for component calculation.
- Gusts: Optional input for sudden wind speed increases that can affect crosswind strength; factoring gusts helps pilots assess real-time conditions.
- Aircraft Crosswind Limit: An optional custom limit for the aircraft’s maximum safe crosswind tolerance to warn pilots when the crosswind is too strong.
- Ground Speed Input (Advanced Use): This input allows flight planners or advanced users to factor in the aircraft’s ground speed for a more precise assessment of wind effects on flight.
- Unit Toggle: Allows switching between knots (kts), kilometers per hour (km/h), or meters per second (m/s) for user convenience and regional preferences.
Providing accurate and comprehensive inputs ensures the wind correction angle tool produces precise results, vital for planning safe takeoffs and landings. This user-friendly interface accommodates both beginners and advanced users for maximum flexibility.
Outputs You Get From the Calculator
When you input the required data, the crosswind landing calculator provides clear, actionable results essential for safe flight planning and operations:
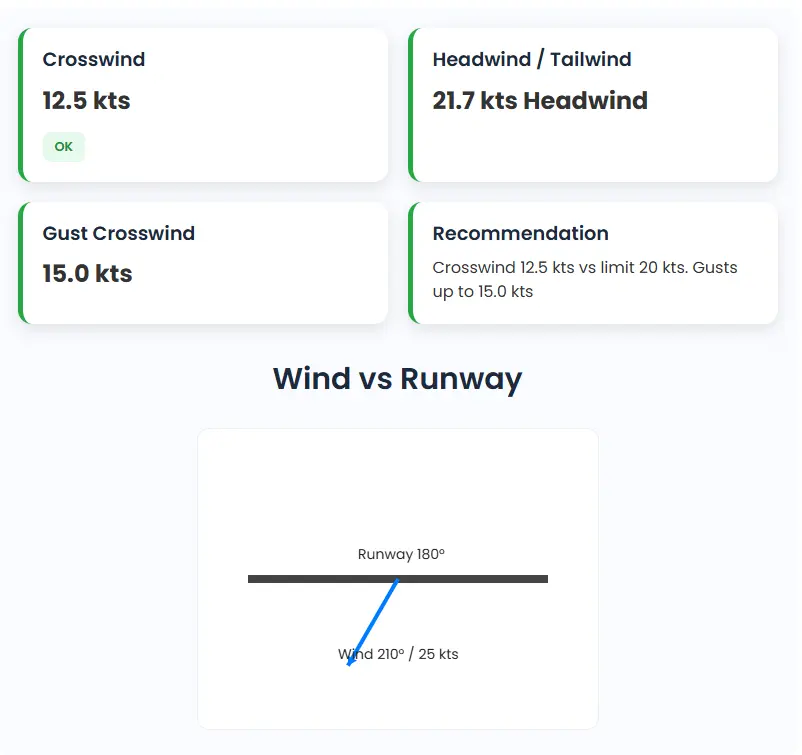
- Crosswind Component (Main): The key result showing the portion of wind blowing perpendicular to the runway, indicating how much sideways force the aircraft will encounter.
- Headwind/Tailwind Component: This output indicates wind blowing directly along the runway axis, either helping (headwind) or hindering (tailwind) takeoff and landing performance.
- Gust Crosswind (If Given): Calculates the crosswind effect of gusts, important for understanding sudden and brief increases in wind force during critical phases.
- Status Badge: A visual indicator that uses color-coded symbols to classify the wind condition into:



- Visual Aids: A graphical representation showing the runway orientation alongside an arrow indicating wind direction and strength, helping users quickly grasp the wind situation.
By offering these outputs instantly, the tool acts as a powerful flight planning crosswind check, helping pilots make informed decisions that prioritize safety and efficiency.
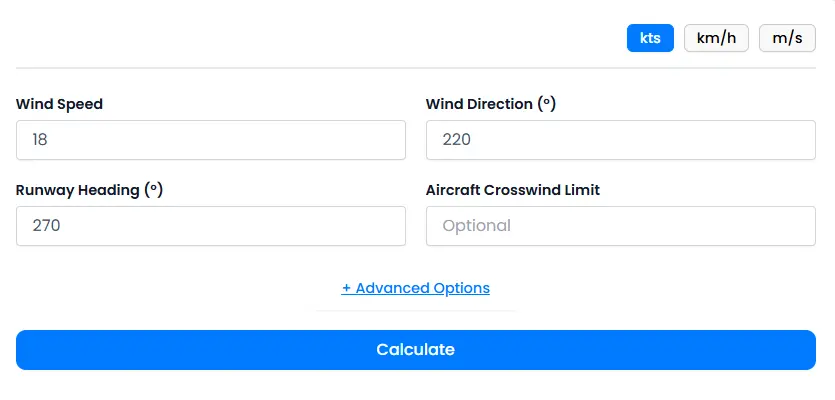
Example Calculation (Step-by-Step)
Let’s walk through how to calculate crosswind and headwind components using a practical example:
- Wind Speed: 18 knots
- Wind Direction: 220°
- Runway Heading: 270° (Runway 27)
Step 1: Calculate the Angle Difference
Angle Difference=∣Wind Direction−Runway Heading∣=∣220−270∣=50∘Angle Difference=∣Wind Direction−Runway Heading∣=∣220−270∣=50∘
Step 2: Calculate Crosswind Component
Use the sine function of the angle difference multiplied by wind speed:
Crosswind=18×sin(50∘)≈18×0.766=13.79 knots Crosswind=18×sin(50∘)≈18×0.766=13.79 knots
Step 3: Calculate Headwind or Tailwind Component
Using the cosine function:
Headwind/Tailwind=18×cos(50∘)≈18×0.642=11.56 knots Headwind/Tailwind=18×cos(50∘)≈18×0.642=11.56 knots
Interpretation:
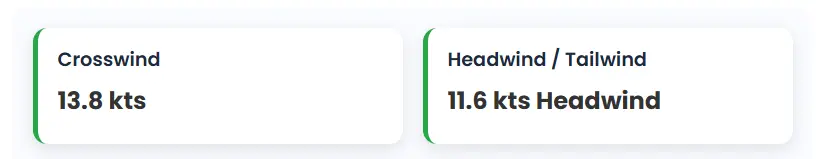
- Crosswind component is about 13.8 knots, meaning the aircraft will face this sideways wind strength during takeoff or landing on Runway 27.
- Headwind component is around 11.6 knots, which can aid the aircraft in reducing ground speed during landing or takeoff.
This step-by-step method provides a clear, formula-based approach to answering “How to calculate crosswind for a runway”, helping pilots make informed, safety-conscious decisions during flight planning.
Practical Applications of the Crosswind Calculator
The Crosswind Calculator serves as a vital tool across various aviation-related fields, helping users improve safety, training, and planning.
- Student Pilot Training (PPL, CPL):
Student pilots rely on the calculator for essential pilot training crosswind practice, helping them understand and manage crosswind challenges during takeoff and landing. - Airline Pilots & Instructors:
Professional pilots and flight instructors use it as a quick reference to ensure safe operation within aircraft limits. The tool supports decision-making by providing accurate wind component data for every flight. - Meteorology Students:
Those studying weather and atmospheric sciences use the calculator to analyze wind effects on flight operations, linking meteorology principles with real-world applications. - Aviation Enthusiasts:
Hobbyists and aviation fans utilize the crosswind calculator app to deepen their knowledge about wind effects on aircraft and to simulate flight scenarios.
Across all these uses, the calculator acts as a reliable online pilot training tool that delivers fast, accurate wind component calculations, making it indispensable for anyone involved in aviation.
FAQ's
What is crosswind in aviation?
How do I calculate headwind and tailwind?
What’s the safe crosswind limit for small aircraft?
Do airline pilots use online wind calculators?
Is this calculator accurate for training?
Conclusion + Call to Action
Using the Crosswind Calculator offers several clear benefits that enhance flight safety and efficiency:
- Faster Flight Planning: Quickly obtain accurate crosswind, headwind, and gust components without manual charts or complex mental math.
- Safer Flights: Know your aircraft’s safe operating limits and assess wind conditions precisely before every takeoff and landing.
- Accessible Learning: The calculator acts as an excellent online tool for student pilots, instructors, and enthusiasts to practice and understand crosswind effects better.
To make the most of your flight preparation and training, bookmark this tool and share it with fellow student pilots and aviation friends. You can also explore more useful tools on our Nux Tools Website.
Use the Crosswind Calculator before every flight planning session to ensure you’re always ready for the wind conditions you’ll face!
Check More Tools:
